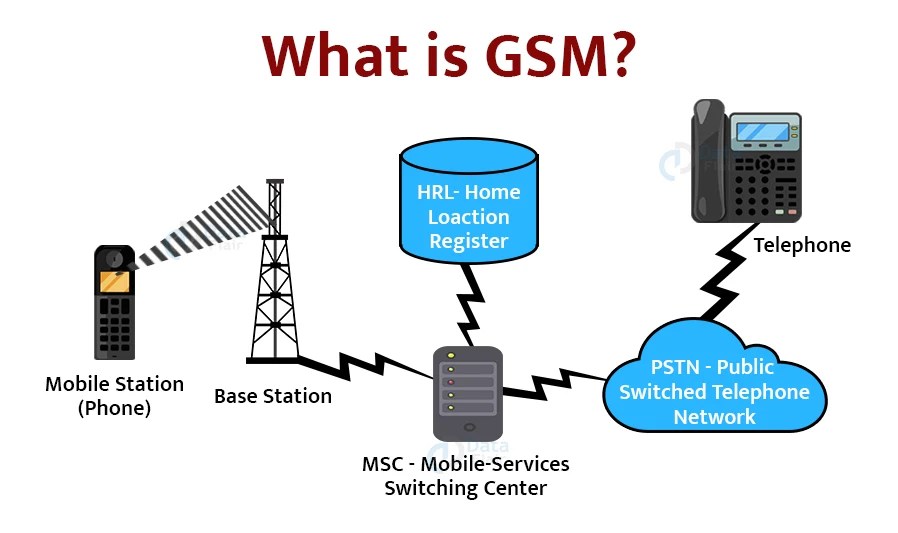
How does the GSM Network work?
The standardized digital cellular network known as GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is utilized for mobile phone service. With more than 5 billion users, it is the most widely used mobile network standard worldwide. The 900 MHz and 1800 MHz frequency bands are used by GSM networks to function.
Text messaging, voice calls, and data services are just a few of the uses for GSM networks. Mobile commerce, mobile payments, and mobile banking are just a few of the many uses for GSM networks.
Comparing GSM networks to other mobile network standards reveals a number of benefits. Different mobile network standards are not as dependable and secure as GSM networks. Additionally, GSM networks are more capable of handling more traffic with less bandwidth than other mobile network standards due to their increased efficiency.
An important factor in the growth of mobile communications has been GSM networks. People can now stay in touch with each other no matter where they are in the world thanks to GSM networks.
Meaning of the GSM Network.
A standardized digital cellular network used for mobile phone calls is called the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications). It is the most widely used mobile network standard in the world, with over 5 billion subscribers. The frequency bands used by GSM networks for operation are 900 MHz and 1800 MHz.
- Global: GSM networks are used in over 220 countries and territories.
- Digital: Voice and data are transmitted over GSM networks using digital technology.
- GSM networks are segmented into discrete geographic regions known as cells.
- Mobile: GSM networks are made to work with portable electronics like cellphones and smartphones.
- Communications: GSM networks are used for a variety of communication purposes, including voice calls, text messaging, and data services.
- Secure: The use of authentication and encryption technologies makes GSM networks secure.
- Dependable: Even in places with weak signal strength, GSM networks are dependable.
GSM networks have played a major role in the development of mobile communications. People can now stay in touch with each other no matter where they are in the world thanks to GSM networks.
International.
GSM networks' worldwide reach is one of their main benefits. Since GSM networks are in use in more than 220 nations and territories, users can remain connected no matter where they are in the globe. People who regularly travel abroad and those on business should pay particular attention to this.
- Ubiquity:. Even in remote places, GSM networks are widely accessible. This implies that users can maintain connectivity even when venturing off the usual route.
- Roaming:. Users of GSM networks can travel between various nations and networks without switching SIM cards. Staying connected when traveling overseas is made simple by this.
- Collaboration:. Because GSM networks are interoperable, customers can use their gadgets on any GSM network globally. Staying in touch with friends and family who reside abroad is made easier by this.
One of the key elements contributing to GSM networks' success is their global reach. People can now stay in touch with each other no matter where they are in the world thanks to GSM networks.
Online.
One of the main benefits of GSM networks is that they are digital. Digital technology is used by GSM networks to transmit data and voice, which has several benefits over analog networks.
- To be clear:. Voice conversations and data transfers are more clear when using digital signals since they are less prone to interference than analog ones.
- Protection:. GSM networks are more secure because digital signals are more difficult to eavesdrop on and intercept than analog signals.
- Efficiency:. GSM networks can send more data in a given amount of bandwidth because digital signals can be compressed more effectively than analog signals.
- Ability:. Digital networks are perfect for use in densely populated areas because they can manage more users and traffic than analog networks.
GSM networks are the most widely used mobile network standard worldwide due to their digital nature. Clarity, security, efficiency, capacity, and other factors are among the benefits that GSM networks have over analog ones.
cellular.
One of the main benefits of GSM networks is their cellular structure. GSM networks can offer a variety of advantages because they are segmented into tiny geographic areas known as cells.
- Reportage:. If wired coverage is not feasible or feasible in a given area, cellular networks can offer coverage in that area. This is particularly crucial in remote and rural areas.
- Ability:. Cellular networks are perfect for usage in densely populated areas because they can manage a lot of users and traffic.
- Mobility:. People can travel freely and remain connected thanks to cellular networks. For mobile devices like cell phones and smartphones, this is crucial.
- Efficiency:. In terms of spectrum usage, cellular networks are effective. This implies that they don't need to use a lot of spectrum to provide a high degree of coverage and capacity.
The GSM standard is the most widely used mobile network in the world due to its cellular nature. Coverage, capacity, mobility, and efficiency are just a few of the benefits that GSM networks have over other mobile network standards.
Portable.
One of the main benefits of GSM networks is that they are mobile. GSM networks enable users to stay connected while they're on the go because they're made for use with mobile devices like smartphones and cell phones. For those who require constant connectivity for work, personal, or security-related reasons, this is imperative.
- Convenience:. Anywhere within the network's coverage area, users of mobile networks can make and receive calls, send and receive text messages, and access data services. For those who are constantly on the go, this is very crucial.
- Efficiency:. When they are not in the office, users can maintain contact with partners, customers, and coworkers through mobile networks. Efficiency and productivity may both benefit from this.
- Security:. In an emergency, mobile networks can be used to make help requests. This can be crucial for those who work in hazardous or remote locations in particular.
The most widely used mobile network standard worldwide is GSM due to its mobile nature. Compared to other mobile network standards, GSM networks have several benefits, such as increased productivity, safety, and ease of use.
Exchange of ideas.
GSM networks are utilized for data services, text messaging, voice calls, and other forms of communication. One of the main factors contributing to GSM's success and popularity is its adaptability.
- phone calls in voice:. One of the most fundamental and important types of communication is voice calls, which are made over GSM networks. Even in locations with weak signal strength, GSM voice calls are dependable and crystal clear.
- Texting someone:. Text messaging is another service that uses GSM networks and is a convenient and rapid means of sending and receiving brief messages. Messenger apps are widely used for business and social media, providing a convenient means of communication with loved ones.
- Information services:. Additional services that let users access the internet and other online resources are data services, which are provided via GSM networks. Downloading apps, checking email, and surfing the web are just a few of the many uses for data services.
GSM networks are useful tools for communication because of their versatility. From conducting business to keeping in touch with loved ones, GSM networks are useful for many things.
Safety.
One of the main benefits of GSM networks is security. Encryption and authentication technologies are used in GSM networks to prevent unauthorized access and eavesdropping on user data.
- Cryptography:. GSM networks encrypt user data to prevent prying eyes. Data is jumbled by encryption to prevent unauthorized parties from reading it.
- Verification:. Authentication technologies are employed by GSM networks to confirm users' identities. Only authorized users are able to access the network and user data thanks to authentication.
To safeguard user privacy and data, GSM networks must be secure. Mobile banking, mobile payments, and mobile commerce are just a few of the uses for GSM networks.". Users are shielded from fraud and identity theft by the security of GSM networks.
trustworthy.
The reliability of GSM networks is one of its key advantages. GSM networks are perfect for use in remote and rural locations because they remain dependable even in areas with weak signal strength.
- Coverage:. Users can maintain connectivity even in remote locations thanks to GSM networks' broad coverage area. Those who work or reside in rural areas should pay particular attention to this.
- Solidity:. GSM networks are resilient to interference and changes in signal strength. This implies that even in places with weak signal strength, users can maintain their connection.
- Handoffs:. Handoffs are a mechanism used by GSM networks to smoothly move calls between various cells. This makes it possible for users to maintain their connection while on the go.
- Duration of battery:. Users can expect extended battery life from their devices thanks to GSM networks' power-efficient design.
For users to have a dependable and consistent mobile experience, GSM network dependability is prerequisite. Text messaging, data services, and voice calls are just a few of the uses for GSM networks. Even in places with weak signal strength, users can maintain connectivity thanks to GSM networks' dependability.
FAQs on GSM Network Meaning.
Questions concerning the meaning of the GSM network are addressed in this section. The purpose of these questions is to dispel common myths and offer a more thorough comprehension of the subject.
First question: What is GSM?
In response:. Global System for Mobile Communications is what GSM stands for.
Question 2: What is the difference between GSM and other mobile network standards?
In response:. GSM is a digital cellular network standard that uses a narrowband frequency range. It is renowned for its dependability, security, and worldwide reach. Different technologies, frequency bands, and capabilities distinguish CDMA, TDMA, and LTE from other mobile network standards.
What benefits come with using GSM networks, third question?
In response:. GSM networks offer several advantages, including:.
Worldwide reach: GSM networks are extensively accessible in more than 220 nations and territories. Reliability: Even in places with weak signal strength, GSM networks are renowned for their stability and resilience. Security: To safeguard user data and communications, GSM networks make use of strong encryption and authentication technologies. GSM networks' interoperability enables smooth roaming between various network providers and nations.4. What are the GSM networks' limitations?
In response:. Although GSM networks have many benefits, they also have certain drawbacks, like the following.
Speed: In comparison to more recent technologies like 4G and 5G, GSM networks transfer data at a slower rate. Capacity: Due to their limited capacity, GSM networks may experience congestion at periods of high usage.Question 5: In the current mobile environment, is GSM still relevant?
In response:. Indeed, GSM networks still have a big impact on mobile technology, especially in developing nations and rural areas. Because of its low cost, dependability, and extensive worldwide coverage, GSM is still widely used even though newer technologies have faster speeds and more capacity. Particularly for simple voice calls and SMS messaging, it is crucial.
Sixth question: How will GSM networks fare in the future?
In response:. For the foreseeable future, it is anticipated that GSM networks and more modern technologies will coexist. They might gradually disappear in developed markets, but in areas with poor infrastructure and low bandwidth needs, they probably won't go away. Furthermore, new uses of GSM technology, like M2M and Internet of Things communication, are being investigated.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:. With their dependable and secure platform for voice calls, text messaging, and data services, GSM networks have completely changed mobile communications. In the global mobile landscape, GSM is still essential, even though newer technologies have better capabilities. This is especially true for basic connectivity and in places with poor infrastructure.
Go on to the following section of the article:. This wraps up our investigation into the significance and essential elements of the GSM network. In the next section, we will delve into the historical development and evolution of GSM technology.
Meaning of the GSM Network.
Examining the meaning of the GSM network has brought to light the importance and broad use of GSM technology in the global mobile environment. With the ability to offer a dependable and secure platform for data services, text messaging, and voice calls, GSM networks have completely changed mobile communications. Due to their interoperability, low cost, and broad reach, billions of people have gained access to them globally.
Even though more recent technologies have better features, GSM is still an essential technology, especially in underdeveloped nations and rural areas with poor infrastructure. It still has a significant impact on enabling basic connectivity and vital services. Furthermore, new uses of GSM technology, like M2M and Internet of Things communication, are being investigated.
In conclusion, GSM networks have had a transformative impact on mobile communications and continue to play a fundamental role in connecting people around the world. Their legacy of reliability, security, and global reach will ensure their continued relevance in the years to come.
.